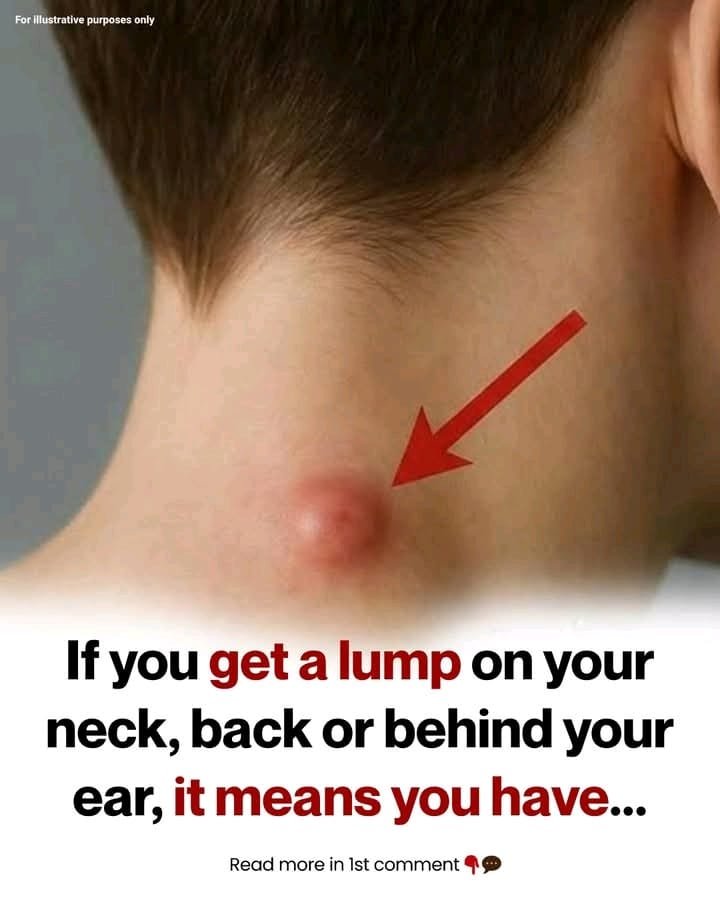
If you notice a new lump on your neck, back, or behind your ear, it does not automatically mean something serious, but it should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the cause.
Most lumps in these areas are benign (non-cancerous) and can be caused by:
-
Swollen lymph nodes – The most common cause. This often happens due to:
-
Infections (like a cold, strep throat, ear infection, or skin infection)
-
A temporary reaction to a nearby infection or inflammation
-
-
Benign cysts – Such as sebaceous cysts or epidermoid cysts, which are slow-growing, fluid-filled sacs under the skin.
-
Lipomas – Soft, fatty lumps that move easily under the skin, usually harmless.
-
Benign skin conditions – Like acne, folliculitis, or boils.
-
Reaction to injury or irritation – From a cut, ingrown hair, or insect bite.
However, in rare cases, a lump can be a sign of something that needs medical attention, such as:
-
Infection that may need antibiotics or drainage.
-
Benign tumors (like certain salivary gland tumors).
-
Malignant tumors (cancer), such as lymphoma, metastatic cancer, or skin cancer (e.g., squamous cell carcinoma).
When to see a doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if the lump:
-
Grows quickly or is larger than 1–2 cm
-
Feels hard, fixed, or immovable
-
Lasts longer than 2–3 weeks
-
Is associated with other symptoms like fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss, difficulty swallowing, or changes in your skin
-
Is painful, red, warm, or draining pus
Bottom line
Don’t panic—most lumps are harmless. But get it checked to be sure. A doctor can usually diagnose it through a physical exam, and sometimes with imaging (ultrasound) or a biopsy if needed. Early evaluation is key for peace of mind and proper treatment if necessary.